Pwd Parking Slot Dimension
In computing for parking slots, a fraction of 50% and above shall be considered as one car parking slot. In areas where adequate public parking lots/multi-floor parking garages are available within 200 m of the proposed building, only 30% of parking requirement need to be provided within their premises. The ordinance revealed a PWD driving a vehicle or a driver with a PWD passenger shall present to the parking attendant the valid PWD identification card issued by the City Social Welfare and Development Office to avail of the PWD parking slot and that the ID card shall be displayed inside the vehicle visible to the public.
Customer service hinges on the ability of an organization to understand and be sensitive to the needs of their customers. Persons with disabilities are paying customers too, no different from everybody else, except for the discounts, which the government reimburses by way of tax incentives. Still it is good business to develop and improve services for all customers, including the Pinoys with disabilities.
- Handicapped Spaces. All handicapped parking spaces shall be provided and designed in accordance with the 2003 American National Standard, as now or hereafter amended. Dimensional Requirements. All parking spaces shall comply with the dimensional standards of Tables 17-1 through 17-4.
- The minimum and maximum dimensions for spaces in the built environment should consider the following criteria: 1.2.1 The varying sizes and statures of persons of both sexes, their reaches and their lines of sight at both the standing and sitting positions. 1.2.2 The dimensional data of the technical aids of disabled persons.
Customer service means that the staff does not discriminate their customers because each sale directly contributes to the store’s and the employee’s livelihood. Even a giant corporation like SM is careful in showing the littlest sign of discrimination in both their employees and their customers. In one viral instance, the manager of SM Telabastagan in Pampanga unceremoniously ejected a group of deaf diners from the food court. Why? Because the group was supposedly too loud and were allegedly disruptive to the other diners.
After that incident went viral, many people got upset with the manager and the management of SM was compelled to issue an apology and perhaps some form of reparation. Without social media, that incident would have gone unnoticed and the manager, unrepentant.
While being called out on social media is one thing, being aware and sensitive to the needs of PWD customers is quite another.
PWD customers are a niche of customers that many companies have ignored until recently when RA 10754 was passed in 2016. Not only were the benefits of PWDs expanded to include VAT exemption, qualification for the PWD ID became another subject of much debate as many are beginning to realize that they are persons with disabilities but have let denial deprive them of their benefits under the law. It wasn’t just a matter of better parking and coding exemptions: it was recognition of their existence and upholding of their rights under the law.
Which again brings us to the question, why do many companies chose to ignore their PWD customers? The most basic answer; they do not know what to do when they encounter a PWD customer. To avoid customer service booboos, they just ignore them entirely and treat them like everybody else. PWDs do want equal treatment but there needs to be context when qualifying the meaning of the term “social equality.” Stairs need to have ramps, PWDs must have a special express lane, parking slots must be reserved for the exclusive use of the PWD and PWDs must be given their 20% discounts and 12% VAT exemption. Not because the service provider is generous, but because it is the law. Business can no longer avoid dealing with PWDs because the law recognizes that we all live together in this beautiful country and, I will not use the term in its proper context, must enforce “social equality.”
So how to give all customers all smiles? By learning more about their clientele, including the PWDs. In 2010, the Philippine Statistics Authority said that 1.7% of the Philippines’ population lives with some form of disability. By 2016, the United Nations says there are 1 in every 7 persons in the world who suffers from some form of disability. We are now more than 100 million and by 2017, it has been estimated by a study commissioned by a foundation for children with autism that the number of PWDs in the Philippines might number up to 10% or higher. The Philippine government has yet to confirm the exact number of Pinoys with disabilities as a study has yet to be done. So how does this affect businesses? Quite heavily.
PWDs, whether they are employed or not, whether they have their own money or not, are spenders. In fact, they are big spenders, sometimes accounting for up to or sometimes more than 50% of a family’s expenditures (according to a survey published by the Disability and Health Journal in Oct 2017). Note than this is not a call for businesses to take advantage of PWDs. This is a call for the need to be aware and sensitive to their needs simply because their caretakers and families are some of a mall’s biggest customers. So it is just right (and legal) to give them good service when they try to buy something.
Here are some of the tips that may be most helpful when working with PWD customers:
1. If a customer shows you a PWD ID, take note of the number and give them the discount they are entitled to. DO NOT PRY into their personal life by making small talk in an effort to know what their medical condition is. Neither should a service provider doubt that the ID might have been given in error as the customer who claims to have a disability may not exactly have one in your opinion. You are not a doctor well enough to judge who has a disability, and which one does not. PWD ID applications are carefully scrutinized before they are given out. Plus the ID numbers are registered with the Department of Health. If in doubt, you may ask the Department of Health, but do not believe that the ID might not be genuine. However in the meantime, the PWD must be given the discount not kept waiting.
2. Do not shout at the deaf or blind people. If they are deaf, no amount of shouting will help. If they are blind, then you not need to shout. Do not be afraid to ask if they prefer to communicate using the written language for the deaf as many of them understand written English and Filipino. But it would be great if a mall or store had someone who knows a little sign language.
3. If the PWD customer is assisted by an interpreter, talk directly to the PWD, not to the interpreter. It is rude to do so.
4. Never assume the preference of the PWD customer on colors, taste and price. Just like any customer, let them choose and decide for themselves.
5. Never touch or assist a PWD if they do not ask for it. Do not move a PWD’s wheelchair without permission. Never assume that seeing eye dogs are just pets, they are more than that. Treat them with the same respect as you would any customer.
If your organization is absolutely unsure of how to deal with PWD customers, call us at PWDPhil (946-2058). Our organization has volunteers that arrange for awareness and sensitivity seminars for your staff and front-liners. Or you may email us at info@pwdphil.com
“AN ACT TO ENHANCE THE MOBILITY OF DISABLED PERSONS
BY REQUIRING CERTAIN BUILDINGS, INSTITUTIONS, ESTABLISHMENTS AND PUBLIC UTILITIES
TO INSTALL FACILITIES AND OTHER DEVICES.”
Joint Promulgated By:
The Department of Public Works and Highways Port Area, Manila
The Department of Transportations and Communications Pasig, Metro Manila
in coordination with:
The National Council for the Welfare of Disabled Persons
(Accessibility Sector on the Magna Carta for Disabled Person) Diliman, Quezon City
RULE I – SCOPE AND APPLICATION
1. Purpose:
The Rules and regulations set forth herein provide for minimum requirements and standards to make buildings, facilities and utilities for public use accessible to disabled persons, pursuant to the objectives of Batas Pambansa Bilang 344, An Act to Enhance the Mobility of Disabled Persons by Requiring Certain Buildings, Institutions, Establishments and Public Utilities to Install Facilities and Other Devices.
2. Definition of Terms:
For the purpose of these Rules and Regulations, the words, terms and phrases enumerated in Annex A hereof shall have the meaning as provided therein.
3. Scope:
The provisions of these Rules and Regulations shall apply to the following:
3.1 Public and private buildings and related structures for public use and which shall be constructed repaired or renovated.
3.2 Streets and highways and public utilities
3.2.1 Streets and highways
3.2.2 Public transport vehicles which shall include:

a). Passenger buses and jeepneys
b). Passengers trains, including those of the Light Rail Transit Authority (LRTA)
c). Domestic inter-island vessels
d). Domestic aircraft of air carriers
3.2.3 Public Telephones
3.3 Public transport
terminals including those of LRTA
4. Application:
4.1 Public and private buildings and related structures for public use.
No permit for the construction, repair or renovation of public and private buildings and related structures for public use, whether owned or leased, shall be granted or issued, unless the owner thereof shall have provided in the places and specifications submitted for approval barrier-free facilities and accessibility features as provided in these Rules and in accordance with the followings criteria:
4.1.1 Building and related structures to be constructed
a). At the space where the primary function is served and where facilities and ingress/egress of the building or structure are located, as to make such space accessible to the disabled persons; provided, however, that where the primary function can be served at the ingress level and where such level is provided with facilities, requirements for accessibility at other levels may be waived.
b). Ten percent (10%) of the total number of units of government-owned living accommodations shall be accessible and fully usable by the disabled persons with any fractional part in excess of one-half (1/2) in the computation thereof, to be considered as one unit; for privately-owned living accommodations the number of accessible units shall be as provided in Section 3 of Rule III thereof.
c). Ingress/egress from the street to the building or structure shall be made accessible.
d). Accessible slots in parking areas shall be located as near as possible to ingress/egress spaces of the building or structure.
4.1.2 Building and related structures to be repaired or renovated including those proposed for a change of occupancy – If feasible , barrier-free facilities and accessibility and accessibility features shall be provided in accordance with the requirements under Subsection 4.1.1 (1), (c ) and (d): feasibility of incorporation of barrier-free facilities and accessibility features shall be determined from all the following conditions:
a). When the repair or renovation work is to be done in the space where the primary function is served;
b). When the facilities can be made accessible at any other level which is accessible by means of an elevator with a minimum width of 800 mm;
c). When the space allotted for the primary function will not be diminished by more than ten percent (10%) of its original area;
d). When the capacity or strength of any major structural component, such as slabs, beams, girders, columns, bearing walls and footing of the building or structure will not be diminished;
e). When the cost (exclusive of the exception provided below) of such repair or renovation work is in excess of twenty percent (20%) of the total cost of the building or structure, based upon the computation of permit fees as provided under Rule III of the Implementing Rules and Regulations promulgated pursuant to P.D. 1096 entitled: The National Building Code of the Philippines;
f). When there is no legal constraint which would not allow compliance with these regulations:
EXCEPTION: Repair or renovation work which consists only of heating, ventilating and air conditioning systems, including those which may be required only with respect to fire panic and explosion safety for existing spaces, shall not be subject to the requirements for barrier-free facilities and accessibility features.
4.2.1 Streets, highways and transport related structures to be constructed – Streets, highways and transport related structures shall be provided with the following barrier-free facilities and accessibility features at every pedestrian crossing: ramps and other accessible features in buildings of the Sectoral offices and attached agencies of DOTC; transportation terminals and passenger waiting areas for use of disabled person;
a) Cut-out curbs and accessible ramps at the sidewalks.
b) Audio-visual aids for crossing
EXCEPTION: Requirements for accessibility at pedestrian grade separations or overpasses and underpasses may be waived.
4.2.2 Existing streets and highways to be repaired and renovated the accessibility requirements shall be provided where the portion of existing streets and highways to be repaired or renovated includes part or the entire pedestrian crossing.
4.2.3 Transport vehicles for public use
a) No license or franchise for the operation of public buses, passenger boats, ships and domestic airplanes shall be granted or issued unless the owner or operator thereof shall have provided and designated the number of seats and shall have placed audio-visual aids.
b) Government instrumentalities operating passenger trains including the Light Rail Transit Authority shall have provided the number of seats for disabled persons.
c) Government instrumentalities operating passenger airplanes shall provide and designate the number of seats for disabled persons and shall likewise place the audio-visual aids
4.2.4 Existing Public Transport Vehicles – The minimum accessibility requirements shall apply to all existing units of public transport vehicles, and including those units, which are to be repaired and renovated.
4.2.5 Public Telephones – At least one unit of public telephones for every four (4) units shall be accessible to disabled persons and shall be provided with visual aids required, provided that if only (1) public telephone is to be installed in a particular place the same shall be accessible to disabled persons.
4.2.6 Public Transport Terminals – The criteria and accessibility requirements, provided for public and private buildings and related structures for public use shall apply to public transport terminals.
5. Special Standards of Accessibility:
Where the requirements for accessibility in the Rules will create an unreasonable hardship in design/construction, special standards of accessibility through the use of other methods and/or materials shall be allowed if better facilities can be provided subject to the approval of the National Council for the Welfare of Disabled Persons..
RULE II – MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR ACCESSIBILITY
1. Design Criteria:
1.1 CATEGORIES OF DISABLED PERSONS. The categories of disability dictate the varied measures to be adopted in order to create an accessible environment for the handicapped. Disabled persons under these Rules may be classified into those who have:
1.1.1 Impairments requiring confinement to wheelchairs; or
1.1.2 Impairments causing difficulty or insecurity in walking or climbing stairs or requiring the use of braces, crutches or other artificial supports; or impairments caused by amputation, arthritis, spastic conditions or pulmonary, cardiac or other ills rendering individuals semi-ambulatory; or
1.1.3 Total or partial impairments of hearing or sight causing insecurity or like hood of exposure to danger in public places; or
1.1.4 Impairments due to conditions of aging and in coordination;
1.1.5 Mental impairments whether acquired or congenital in nature.
1.2 ANTHROPOMETRICS AND DIMENSIONAL DATA AS GUIDES FOR DESIGN.
The minimum and maximum dimensions for spaces in the built environment should consider the following criteria:
1.2.1 The varying sizes and statures of persons of both sexes, their reaches and their lines of sight at both the standing and sitting positions.
1.2.2 The dimensional data of the technical aids of disabled persons. Included in the second consideration are the dimensions of wheelchairs; the minimum spaces needed for locking and unlocking leg braces plus the range of the distance of crutches and other walking aids from persons using such devices. By applying at this very early stage dimensional criteria which take into account wheelchair usage, the physical environment will ultimately encouraged and enable wheelchair users to make full use of their physical surroundings.
1.2.3 The provision of adequate space for wheelchair maneuvering generally insures adequate space for disabled persons equipped with other technical aids or accompanied by assistants. In determining the minimum dimensions for furniture and fixtures accessible to disabled persons, the following anthropometrics data shall serve as guides for design: The length of wheelchairs varies from 1.10 m to 1.30 m . The width of wheelchairs is from 0.60 m to 0.75 m. A circle of 1.50 m in diameter is a suitable guide in the planning of wheelchair turning spaces. The comfortable reach of persons confined to wheelchairs is from 0.70 m to 1.20 m above the floor and not less than 0.40 m from room corners. The comfortable clearance for knee and leg space under tables for wheelchair users is 0.70 m. Counter height shall be placed at a level comfortable to disabled persons’ reach.
1.3 BASIC PHYSICAL PLANNING REQUIREMENTS. No group of people shall be deprived of full participation and enjoyment of the environment or be made unequal with the rest due to any disability. In order to achieve this goal adopted by the United Nations, certain basic principles shall be applied:
1.3.1 ACCESSIBILITY. The built environment shall be designed so that it shall be accessible to all people. This means that no criteria shall impede the use of facilities by either the handicapped or nondisabled citizens.
1.3.2 REACHABILITY. Provisions shall be adapted and introduced to the physical environment so that as many places or buildings as possible can be reached by all.
1.3.3 USABILITY. The built environment shall be designed so that all persons, whether they be disabled or not, may use and enjoy it.
1.3.4 ORIENTATION. Finding a person’s way inside and outside of a building or open space shall be made easy for everyone.
1.3.5 SAFETY. Designing for safety insures that people shall be able to move about with less hazards to life and health.
1.3.6 WORK ABILITY AND EFFICIENCY. The built environment shall be designed to allow the disabled citizens to participate and contribute to developmental goals
RULE III – SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR BUILDINGS AND RELATED STRUCTURES FOR PUBLIC USE
1. CLASSIFICATION OF BUILDING BY USE OF OCCUPANCY:
1.1 Occupancy classified by categories enumerated in Section 710 of the National Building Code (PD 1096) are hereby adapted
1.1.1 Category I – Residential – This shall comprise Group A and partly Group b Buildings
1.1.2 Category II – Commercial and Industrial – This shall comprise partly Groups B, C, E, F, G, H, AND I Buildings
1.1.3 Category III – Educational and Industrial – This shall comprise partly Group C, D, E, and H Buildings
1.1.4 Category IV – Agriculture – This shall comprise partly Group J Buildings.
1.1.5 Category V – Ancillary – This shall comprise partly Group J Buildings.
2. ARCHITECTURAL FEATURES AND FACILITIES: Where the following features and facilities are: architectural design requirements in accordance with generally accepted architectural practice, the same include the corresponding graphic signs.
2.1 Architectural facilities and features:
2.1.1 A – Stairs
2.1.2 B – Walkways
2.1.3 C – Corridors
2.1.4 D – Doors and Entrance
2.1.5 E – Washrooms and Toilets
2.1.6 F – Lifts/Elevator
2.1.7 G – Ramps
2.1.8 H – Parking Areas
2.1.9 I – Switches, Controls, Buzzers
2.1.10 J – Handrails
2.1.11 K – Thresholds
2.1.12 L – Floor Finishes
2.1.13 M – Drinking Fountains
2.1.14 N – Public Telephones
2.1.15 O – Seating Accommodations
3. CATEGORY I The following requirements shall only apply to government-owned building:
3.1 Group A
3.1.1 Single detached. Ten percent (10%) of the total units to be constructed. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, and L.
3.1.2 Duplexes: Ten percent (10%) of the total units to be constructed. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, and L.
3.1.3 School or company staff housing units: One (1) unit for 26 to 50 units to be constructed and 1 additional unit for every 100 units thereafter. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, and M.
4. Category II The following requirement shall apply to both government and privately owned buildings.
4.1 Group B
4.1.1 Accessories, tenement houses and/or row houses, apartment houses and/or town houses. One (1) unit for every 50 units up to 150 units and an additional unit for every 100 units thereafter. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, and L.
4.1.2 Hotels, motels, inns, pension houses and/or apartels. One (1) unit per every 50 units up to 150 units and additional unit for every 100 units at ingress level. In case there is no barrier-free elevators: at least one (1) unit shall be provided at ingress level. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, and N.
4.1.3 Private or off campus Dormitories: One (1) unit per every 50 unit up to150 units and additional dwelling unit for every 100 units thereafter at ingress level. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, and N.
4.2 Group C
4.2.1 Amusement Halls and Parlor Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.2.2 Massage and Sauna Parlors Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M.
4.3 Group E-1
4.3.1 Train Stations and Terminals Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.3.2 Bus depots and Terminals Barrier-free facilities required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.3.3 Transportation Office Barrier-free facilities required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.3.4 Airport terminal buildings, heliports Barrier-free facilities required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.3.5 Ports and harbor facilities, landing piers, sheds, ferry landing stations Barrier-free facilities required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.4 Group E-2
4.4.1 General wholesale and retail stores Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, and N.
4.4.2 Shopping centers and supermarkets and public markets Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, and N.
4.4.3 Restaurants, dining and drinking establishments Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, and N.
4.4.4 Office buildings Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, and N.
4.4.5 Financial Institutions Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, and N.
Pwd Parking Slot Dimensions
4.4.6 Funeral parlors, morgues and crematories Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.4.7 Memorial and Mortuary Chapels Barrier-free facilities and features required in A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.5 Group H-I, Group H-4, and Group I
4.5.1 Theaters, Auditoriums and Convention Halls Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
4.5.2 Concert Halls and Opera Houses Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O
4.5.3 Colisea and Sports Complex and Stadiums Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O
4.6 Group F
4.6.1 Dairies and Creameries Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M.
4.6.2 Factories and workshops using incombustible or non-explosive materials Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M.
4.6.3 Breweries bottling plants, canneries and tanneries Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M.
4.7 Groups G-3
4.7.1 Wood working establishments, lumber and timber yards. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, L, L, and M.
4.7.2 Pulp, paper and paper board factories Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, L, L, and M.
4.7.3 Textile and fiber spinning mills Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, L, L, and M.
4.7.4 Garment and undergarment factories Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, L, L, and M.
5. CATEGORY III
5.1 Group C
5.1.1 Educational institutions (schools, colleges, universities, vocational schools, seminaries and novitiates), including school auditoriums, gymnasia, reviewing stands, little theaters and concert halls. Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
5.1.2 Libraries, museums, exhibition halls and art galleries Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
5.1.3 Civil Centers Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
5.1.4 Clubhouses lodges Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, and O.
5.2 Group D-I
5.2.1 Mental hospitals, mental sanitaria, mental asylums Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M.
5.2.2 Jails, prison, reformatories, correctional institutions Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.2.3 Rehabilitation Centers Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.2.4 Leprosaria Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.3 Group D-2
5.3.1 Homes for the Aged Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.3.2 Hospitals and Sanitaria Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.4 Group D-3
5.4.1 Nursing Homes for ambulatory patients Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.4.2 Orphanages Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.5 Group E-7
5.5.1 Police and fire stations Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, and M
5.6 Group H
5.6.1 Churches, temples, chapels and similar places of worship Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, E, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, and O.
6. CATEGORY IV
6.1.1 Agricultural buildings Barrier-free facilities and features required in: A, B, C, D, G, H, I, J, K, and L.
7. STANDARD OF ACCESSIBILITY FOR SPECIAL TYPE OF FACILITIES
7.1 The provision of this section shall apply to the specified type of facilities and identified specific requirements for accessibility and usability which shall be provided for each of the listed occupancy uses.
a) Seating for the disabled shall be accessible from the main lobby to primary entrances, together with related toilet facilities.
b) In all assembly places where seating accommodation is provided, there shall be spaces for the disabled persons as provided. Seating Capacity Wheelchair Seating Space
4 – 50 2
51 – 300 4
301 – 500 6
c) When the seating capacity exceeds 500 an additional wheelchair seating space shall be provided for each total seating capacity increase of 100 seats.
d) Readily removable seats may be installed in these spaces when such spaces are not required to accommodate wheelchair users.
8. COMPUTATION OF ACCESSIBLE UNITS
In the computation for the allocation of accessible units and seating capacity decimal greater than 0.5 shall be considered as one unit. In all cases a minimum of one (1) accessible unit shall be provided.
9. APPLICATION OF BARRIER-FREE FACILITIES AND FEATURES
9.1 Graphic signs shall be bold and conspicuously installed in every access from point of entry to connecting destination.
9.2 Walkways shall be provided with adequate passageway in accordance with provision.
9.3 Width of corridors and circulation system integrating both and vertical access to ingress/egress level of the building shall be provided.
9.4 Doors and entrances provided herein used as entry points at entrance lobbies as local points of congregation shall be designed to open easily or accessible from floor or to any point of destination.
9.5 Washroom and toilets shall be accessible and provided with adequate turning space.
9.6 Whenever elevator/s is required it should meet the requirements provide.
9.7 Ramps shall be provided as means of access to level of change going to entry points and entrances, lobbies influenced by condition of location or use.
9.8 Parking areas shall be provided with sufficient space for the disabled persons to allow easy transfer from car park to ingress/egress levels.
9.9 Height above the floor or switches and controls shall be in accordance with the provisions.
9.10 Handrails shall be provided at both sides of ramps.
9.11 Floors provided for every route of the wheelchair shall be made of nonskid material.
9.12 Water fountains shall be installed as required. (Refer to Appendix A for the illustrations of Rules II and III complementing Rule II of the previous implementing rules and regulations).

RULE IV – REQUIREMENTS FOR PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION
1. Classification of public conveyances by mode of transport shall be as follow:
1.1 Land Transportation – This shall refer to buses having a minimum seating capacity of 50 persons for regular buses and 40 persons for airconditioned buses. This shall include regular city buses, regular provincial buses, air-conditioned by city buses (Love Bus and Pag-ibig Bus) and air conditioned tourist and provincial buses.
1.2 Rail Transportation – This shall refer to the three railways systems in the country, the Philippine National Railways (PNR) operating in Luzon, the Panay Railways Corporation (PRC) operating in the island of Panay and the Light Rail Transit Authority (LRTA) operating in Metro Manila.
1.3 Water Transportation – This shall refer to domestic passenger ships, ferryboats and other water transportation vessels.
1.4 Air Transportation – This shall refer to the domestic passenger airplanes.
2. No franchise or permit to operate public transportation units shall be granted issued or renewed unless such units are constructed or renovated in accordance with the requirements.
3. If feasible, all owners or operators of existing public transport utilities shall modify or renovate their units to accommodate disabled persons.
4. The construction or renovation of public transport utilities covered by these rules shall be subject to compliance with the body designs and specifications as provided under existing rules and regulations.
5. Posters or stickers shall be conspicuously displayed inside the units.
6. Public transportation shall have designated seats for disabled persons.
6.1 Regular buses shall have at least five (5) designated seats for disabled persons near exit/entrance doors.
6.2 First class, premiere and air-conditioned buses shall have at least four (4) designated seats for disabled persons near the door.
6.3 Passenger trains shall have at least six (6) designated seats per car for disabled persons nearest to the door.
6.4 Passenger airplanes shall have at least two (2) designated seats for disabled persons near the front exit/entrance door on a per aircraft-type basis.
6.5 For regular and air-conditioned city buses, other passengers may use these designated seats if not occupied and yield them to incoming disabled persons whenever the occasion arises.
6.6 For provincial buses, regular and air-conditioned buses, passenger trains and airplanes, the designated seats for disabled persons may be occupied by other passengers only if no disabled persons shall occupy these seats at the start of the trip.
6.7 Jeepneys shall have at least two (2) seats; preferably the front seats as designated seats for disabled persons.
6.8 For jeepneys, other passengers may be use these designated seats if not occupied and yield them to incoming disabled passengers only if the yielding passenger can still be accommodated at the back
6.9 In domestic shipping, each vessel shall:
a. Allocate on a per class-basis, areas for disabled passengers. These areas shall be nearest to the entrance and/or exit doorways of the vessels.
b. Give priority to disabled passengers embarkation and disembarkation through the assignment of time windows. Disabled passengers shall be given a twenty (20) minute period to embark ahead of the three (3) hour embarkation time prior to the ship’s departure; and shall be allocated a maximum of one (1) hour for disembarkation after the ship’s arrival.
7. The designated seats shall be identified by the International Symbol of Access.
8. Owners or operators of city buses operating in highly urbanized cities shall install in their units audiovisual aids such as buzzer, bell, flashing light to inform the driver of any alighting passenger.
9. At least one deck in passenger ships shall be provided with accessible ramps, passageway, access to gangways, galleys, safety equipment and bunks/berths/cabins with dimensions conforming with the requirements.
RULE V – ADMINISTRATION AND ENFORCEMENT
1. Responsibility for Administration and Enforcement
The administration and enforcement of the provision of these Rules and Regulations shall be vested in the Secretary of Public Works and Highways and the Secretary of transportation and Communications, in accordance with the functions and jurisdiction of their respective Departments as provided for by laws as follows.
1.1 The Secretary through the Heads of attached agencies of the Department of Public Works and Highways, with the technical assistance of the Building Research Development Staff, shall administer and enforce the provisions of these Rules and Regulations through the City/Municipal Engineer who shall also act as Local Building Official pursuant to Section 477 of R.A. 7160, otherwise known as the Local Government Code of 1991 and as applied for the following:
1.1.1 Buildings and related structures including public transport terminals
1.1.2 Streets and Highways
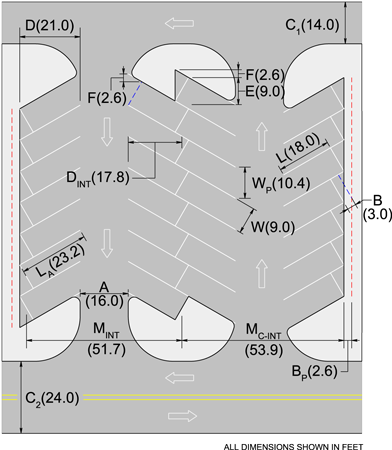
1.2 The Secretary of transportation and Communication shall administer and enforce the provisions of these Rules and Regulations through the Heads of Line and Attached Agencies of the Department as follows:
Pwd Parking Slot Dimension
1.2.1 Land Transportation Franchising and Regulatory Board – In respect to the issuance of Certificate of Public Convenience (CPC) and Provisional Authority (PA) for the operation of public road transportation utilities or services.
1.2.2 Land Transportation Office – In respect to the registration of buses and jeepneys and enforcement of regulations related to land transport.
1.2.3 Philippine National Railways and the Light Rail Transit Authority – For the operation of passenger trains and including stations and terminals.
1.2.4 Maritime Industry Authority – In respect to the development promotion, and regulation of all enterprises engaged in business of designing, constructing, manufacturing, acquiring, operating, supplying, repairing and/or maintaining vessels or components thereof; of managing and/or operating shipping lines, shipyards, dry docks, marine railways, marine repair shops, shipping and freight forwarding agencies and similar enterprises; issuance of license to all water transport vessels.
1.2.5 Philippine Ports Authority – In respect to the planning, development, financing, construction, maintenance and operation of ports, port facilities, port physical plants, and all equipment used in connection with the operation of a port.
1.2.6 Civil Aeronautics Board – In respect to the supervision and regulation of, the jurisdiction and control over air carriers, general sales agents, cargo sales agents and airfreight for warders, and issuance of certificates/licenses to aircrafts.
1.2.7 Air Transportation Office – In respect to the maintenance, operation and development, of all government airports (other than the NAIA, Mactan International Airport) as well as air navigation facilities (excluding meteorology).
2. Criminal Liability
As stipulated in Section 46 of R.A. 7277, otherwise known as the Magna Carta for Disabled Persons
(a), any person who violates any provision of the rules and regulations of this Act shall suffer the following penalties:
1) For the first violation, a fine of not less than Fifty thousand pesos (P50, 000.00) but not exceeding One hundred thousand pesos (P100, 000.00) or imprisonment of not less than six (6) months but not more than two (2) years, or both at the discretion of the court; and
2) For any subsequent violation, a fine of not less than One hundred thousand pesos (P100, 000.00) but not exceeding Two hundred thousand pesos (P200, 000.00) or imprisonment for not less than two (2) years but not more than six (6) years, or both at the discretion of the court.
(b) Any person who abuses the privileges granted herein shall be punished with imprisonment of not less than six (6) months or a fine of not less than Five thousand pesos (P50, 000.00), or both, at the discretion of the court.
(c) If the violator is a corporation, organization or any similar entity, the officials thereof directly involved shall be liable therefore.
(d) If the violator is an alien or a foreigner, he shall be deported immediately after service of sentence without further deportation proceedings.
PERSONS/INDIVIDUALS LIABLE FOR ANY VIOLATION OF THE ACT
For Buildings/Establishment/Structure
Owner or Operator of the Building, Establishment or Structure
Contractor
Architect
Engineer
Building Official or Other Public Official in-charge with the issuance of building permit, registration, certification and/or inspection of the building, establishment or structure
For Air, Land and Sea Transportation
Owner/Operator of Public Transportation
Body builders
Safety Officers/Engineering/Managers
Drivers/Conductors/Conductresses
Public Official in-charge with the issuance of permits, registration, certification and inspection of the public transportation
EFFECTIVITY
These Rules shall take effect thirty (30) days After the date of publication in the Official Gazette
(SGD) JESUS B. GARCIA, JR.
Secretary
(SGD) GREGORIO R. VIGILAR
Secretary
Department of Public Works and Highways
Pwd Parking Slot Dimensions Meters
In coordination with:
The NATIONAL COUNCIL FOR THE WELFARE OF DISABLED PERSONS
By:
(SGD) CORAZON ALMA G. DE LEON
Chairman